Special stains
“BioVitrum” Company develops and manufactures wide range of ready-to-use solutions and kits for histology routine and special staining.
Our benefits:
- High-quality solutions
- Suitable for both manual and automatic staining
- No prior filtration is needed
- Different package sizes
- Perfect differentiation
- High efficiency

We provide a large number of solutions and kits for histology special staining methods. Small 40-100 tests kits for manual staining and big volume kits for automatic staining. Single solutions are also available.
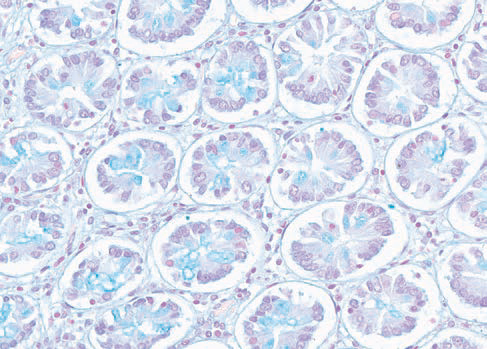
Alcian blue pH 2.5
Method for acid mucopolysaccharides.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-069. |
100 tests |
|
21-069/L. |
3 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Acid mucopolysaccharides - turquoise-blue; nuclei - red.
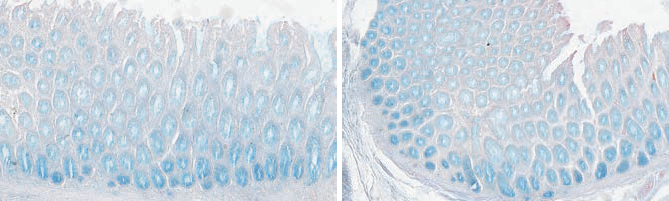
Alcian blue pH 2.5 – pH 1.0
Combined method to distinguish between acid mucins, neutral mucins and carbohydrates.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-017. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Acid mucopolysaccharides - turquoise-blue.
Alcian blue pH 2.5 PAS
Combined method to distinguish between acid mucins, neutral mucins and carbohydrates.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-070. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
PAS-positive substance bright red; acid mucopolysaccharides turquoise-blue; nuclei - blue.
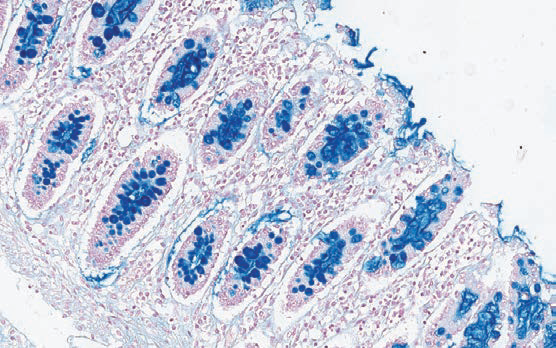
Colloidal iron acc. Mowry
Method for acid mucins.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-027. |
12 assays |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 15-25°C
Results:
Acid mucins – blue; nuclei –red.
Congo red
Method for staining amyloid in tissue sections. Also suitable for polarizing microscopy.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-048. |
100 tests |
|
21-048/L. |
4 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Amyloid – brick red, birefringent in polarized light; nuclei – from blue to violet.
Giemsa for Helicobacter pylori
Method to detect Helicobacter pylori in sections
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-023. |
5 x 150 ml |
|
21-023/L. |
5 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Helicobacter pylori – blue, in form of seagull’s wings; nuclei – blue; cytoplasm - pink.
Gram stain
Method for distinguishing Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-043. |
100 tests |
|
21-043/L. |
5 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Gram-positive bacteria – blue; Gram-negative bacteria – red; nuclei – red.
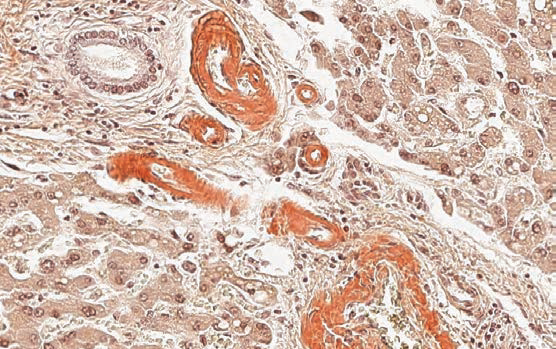
Grocott
Method for staining fungi in tissue sections. Requires incubator.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-063. |
60 tests |
Product validity: 1 years
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
Fungi – sharply delineated in black; mucins – dark gray; background - green.
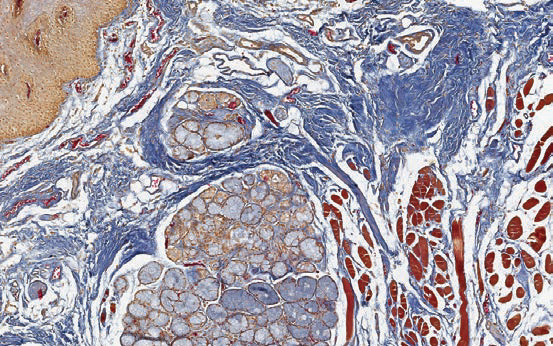
Heidenhain’s azan
General connective tissue method.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-041. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Collagen, reticular fibers, basophilic granules of hypophysis, juxtaglomerular granules and kidney glomerular stroma - dark blue; neuroglia – dark red; muscle – orange; chromatin, erythrocytes, acidophilic granules of hypophysis – red; cytoplasmatic granules of hypophysis delta cells – light blue.
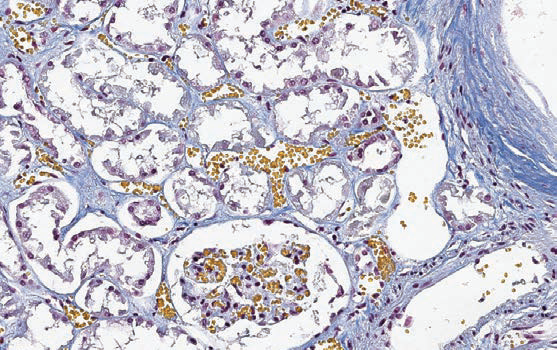
Mallory trichrome
Standard three-color method for connective tissues
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-032. |
100 tests |
|
21-032/L. |
5 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Nuclei, muscle fibers, neuroglia, cartilage, bone – red; collagen fibers - dark blue; erythrocytes, myelin - gold yellow; elastic fibers - pale pink, yellow or unstained.
Masson’s trichrome
Three-color staining with aniline blue.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-042. |
100 tests |
|
21-042/L. |
6 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Nuclei and gametes – black; cytoplasm, keratin, muscle fibers, acidophil granules – red; collagen, basophilic granules of hypophysis- blue; erythrocytes - yellow.
In this video we talk about Masson trichrome, which is widely used to study muscular, cardiac, hepatic or kidney pathologies. Trichrome stain - is a histological staining method which uses two or more acid dyes in combination with a "polyacid" to differentially stain two basic materials in contrasting colors.
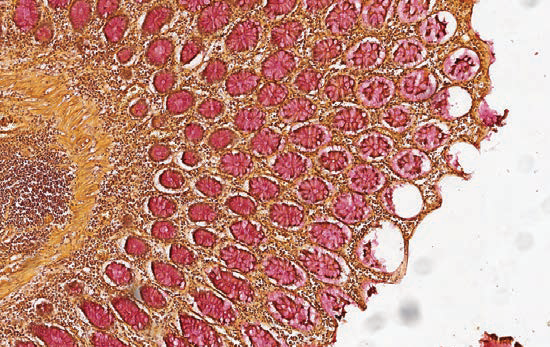
Mucicarmine
Method for staining epithelial acid mucopolysaccharides (mucins).
| Code |
Volume |
|
21-039. |
100 tests |
|
21-062. |
3 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Mucopolysaccharides - from pink to red; nuclei – blue; background - yellow.
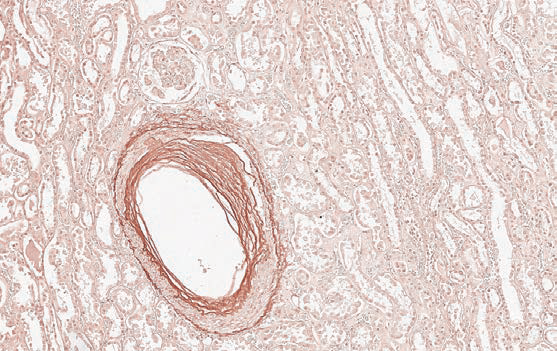
Orcein
Method for elastic fibers.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-034. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Elastic fibers - from dark red to brown; background – almost colorless.
P.A.S. Periodic acid Schiff
The most versatile and widely used technique for carbohydrates or glycoconjugates.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
07-010/S. |
100 tests |
|
07-010/M. |
5 x 250 ml |
|
07-010/L. |
5 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
PAS-positive substance bright red; nuclei - blue.
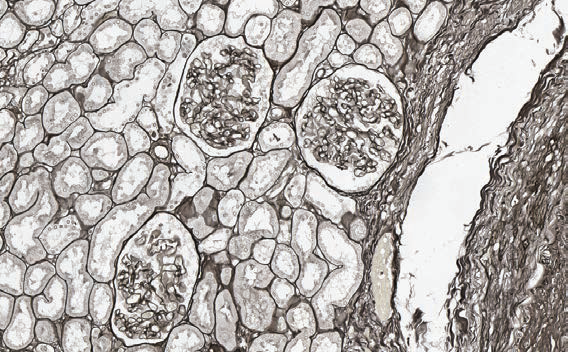
Periodic acid-methenamine silver (P.A.S.M.)
Method for basement membranes. Requires incubation at 60°C.
Warning: Use only distilled or deionized water. All glassware used in this procedure should be chemically cleaned and rinsed thoroughly in distilled water. Do not use metallic tools in this protocol (forceps, tweezers, etc.)
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-028. |
100 tests |
|
21-028/L. |
6 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
Basement membranes, glycogen, mycetes and bacterial capsule – black.
Perl’s Prussian blue iron
Method to detect and identify ferric iron (Fe3+).
|
Code |
Volume |
|
07-004. |
3 x 250 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Ferric iron (Fe3+) – blue; nuclei – red.
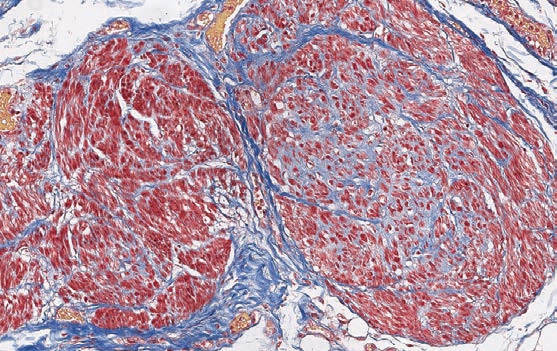
Picro Mallory trichrome
Modified Mallory method.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-036. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Nuclei - dark-brown; collagen fibers - dark blue; cartilage, bone, mucopolysaccharides, basophilic granules of hypophysis, amyloid - various shades of blue; fibrogliya, neuroglia, fibrin, axial cylinders – red; acidophilic granules of hypophysis – orange; myelin and erythrocytes – yellow; elastic fibers - from pale pink to yellow.

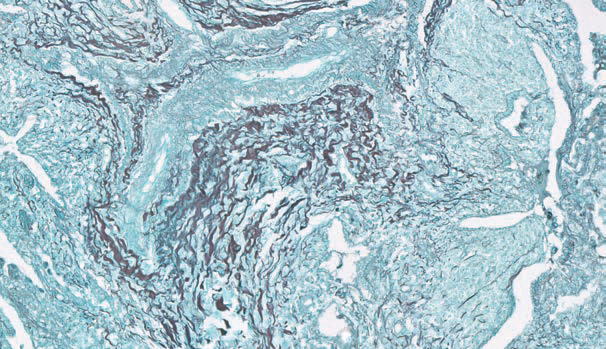
Silver impregnation
Method for reticular fibers.
Warning: Use only distilled or deionized water. All glassware used in this procedure should be chemically cleaned and rinsed thoroughly in distilled water. Do not use metallic tools in this protocol (forceps, tweezers, etc.)
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-026. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
Reticular and nerve fibers – black; connective tissue- brown; collagen - gold yellow.
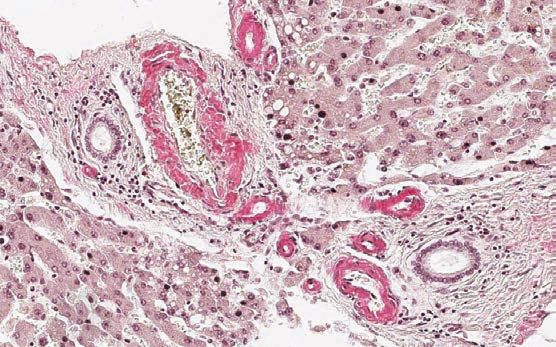
Sirius red
Method for staining amyloid in tissue sections.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-040. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Amyloid – pink-red; nuclei –blue.
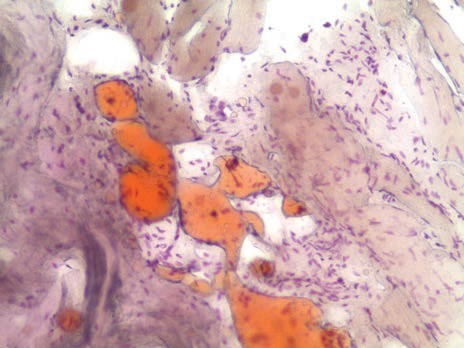
Sudan III acc. Herxheimer
Method to demonstrate lipids in cryostat tissue sections.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-065. |
150 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Lipids – from orange to red.
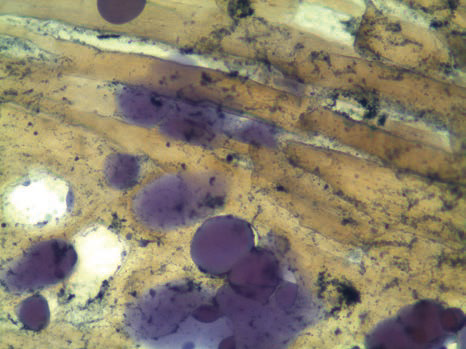
Sudan black
Method to demonstrate lipids in cryostat tissue sections.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-066. |
150 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Lipids – black.
Van Gieson trichrome
Traditional method for connective tissues
|
Code |
Volume |
|
01-001/S. |
100 tests |
|
07-001\L. |
3 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Nuclei – black; collagen fibers - purple-red; cytoplasm, smooth and striated muscle, cornified epithelium, neuroglia and erythrocytes - yellow.
Van Gieson staining is the most common histological method of differential staining of collagen in connective tissue. It used to study pathological changes in bones, cartilages, tendons, derma and blood vessels. Collagen makes up to 35% of the whole-body protein content. That's why its visualization is important for studying pathological processes in tissues.
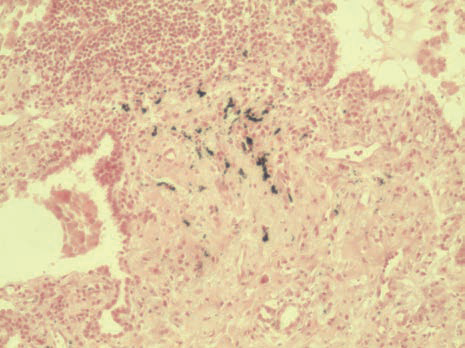
Von Kossa
Staining method for calcium in histological sections.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-066. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 1 year
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
Sites calcium deposits – black; nuclei – red.
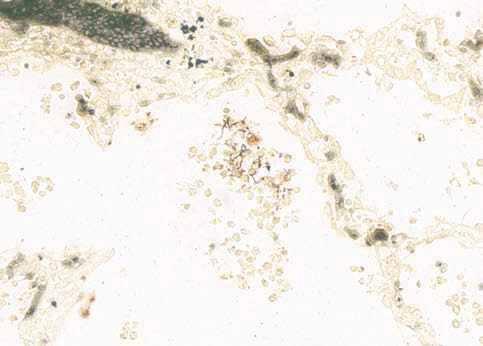
Warthin-Starry
Method to detect spirochetes and other microorganisms. Requires incubator.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-019. |
40 tests |
Product validity: 1 years
Storage temperature: 2-8°C
Results:
Spirochetes and other microorganisms – black; background – gold brown.
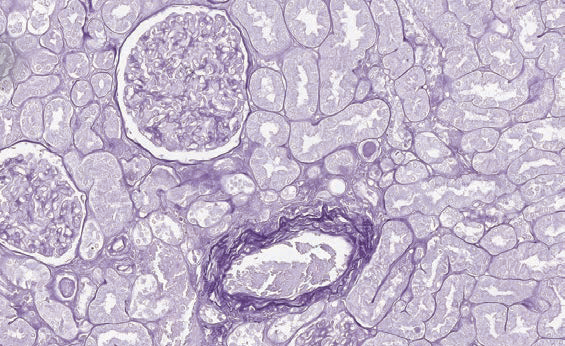
Weigert for elastic fibers (long method)
Method for staining elastic fibers. Requires overnight incubation.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-030. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Elastic fibers - from dark blue to black.
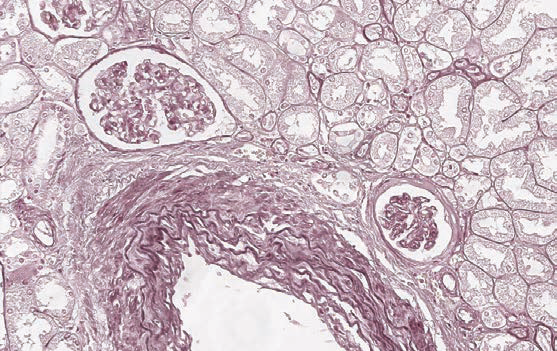
Weigert for elastic fibers (express method)
Method for staining elastic fibers.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-031. |
100 tests |
|
21-031/L. |
4 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Elastic fibers red-brown; nuclei - red.
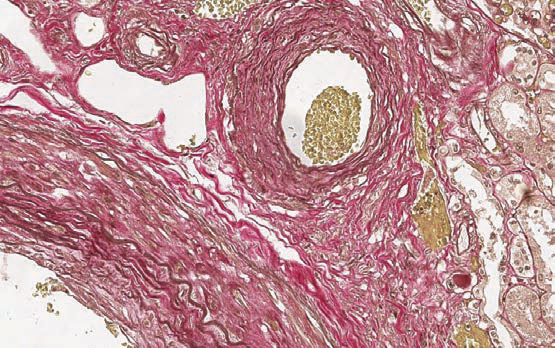
Weigert – Van Gieson (long method)
Method for simultaneously staining elastic fibers, connectivum, collagen and nuclei. Requires overnight incubation.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-020. |
100 tests |
|
21-020/L. |
5 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Elastic fibers - from dark blue to black; nuclei – black; collagen - various shades of red; background and erythrocytes - yellow.
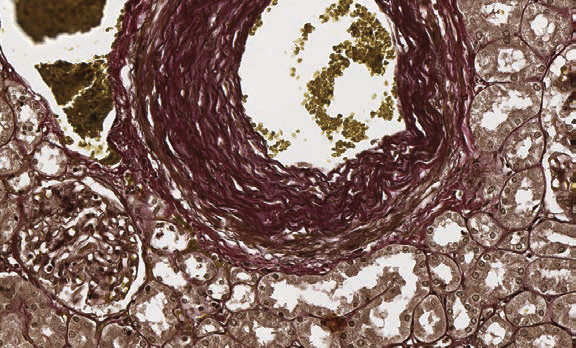
Weigert – Van Gieson (express method)
Method for simultaneously staining elastic fibers, connectivum, collagen and nuclei.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-021. |
100 tests |
|
21-021/L. |
5 x 1000 ml |
Product validity: 2 years
torage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Elastic fibers - from purple-red to brown; nuclei – black; collagen - various shades of red; background and erythrocytes - yellow.
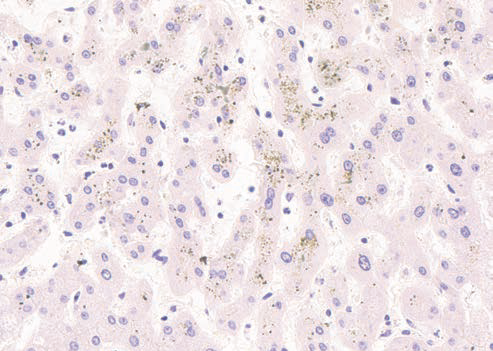
Wilson’s disease staining kit
Method for staining copper in tissue sections. Requires incubator.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
21-064. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Copper – red, red-orange; nuclei – blue.
Ziehl-Neelsen
Method for staining pathogenic mycobacteria.
|
Code |
Volume |
|
07-012/S. |
100 tests |
Product validity: 2 years
Storage temperature: 5-25°C
Results:
Koch’s bacillus and other acid resistant elements – red; background - blue.
Here we discuss histological staining for visualization acid-fast bacteria in tissues - Ziehl-Neelsen staining. Tuberculosis is an infectious disease, which is a huge problem all over the world and roughly one third of the world population is infected with it. It is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis - acid-fast bacteria.